Transition probabilities for the four possible states of two lineages within a subpopulation.#
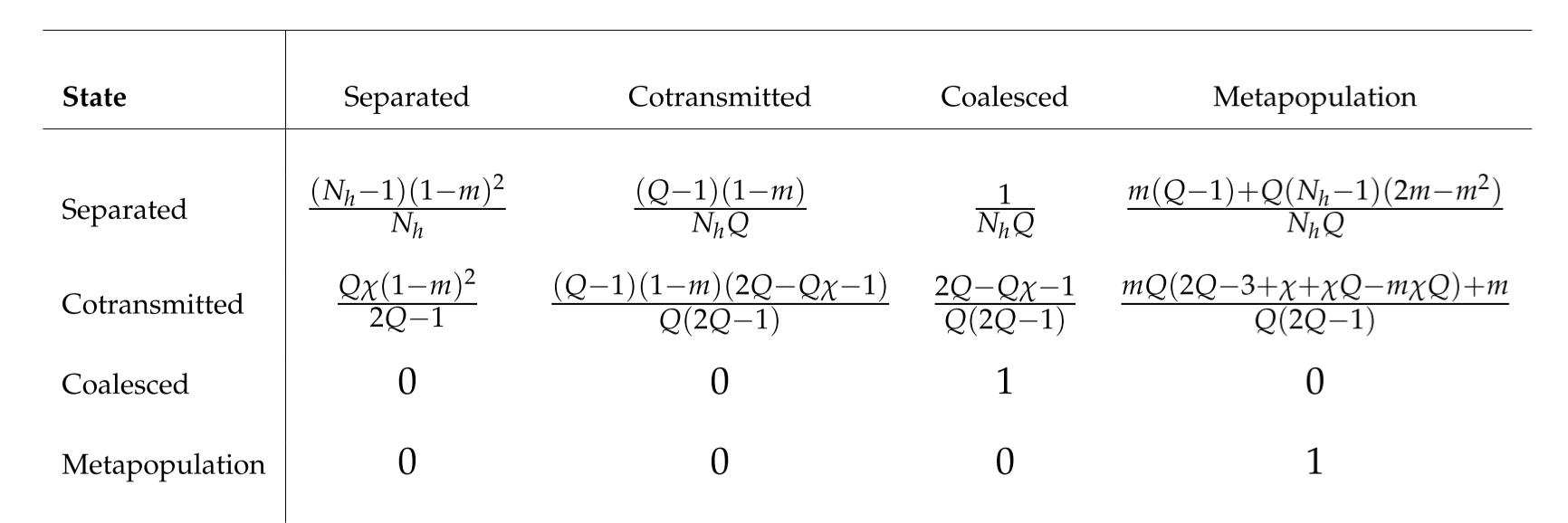
At any point in time, two lineages must be (1) separated within the subpopulation or (2) cotransmitted within the subpopulation or (3) coalesced within the subpopulation or (4) entered the metapopulation. m is the probability that a host within the local subpopulation acquired their infection from the metapopulation. If the metapopulation is much larger than the subpopulation then we can treat it as an absorbing state. Row i column j of the table gives the probability that lineages in state i will transition to state j if we go back a single generation.