Heterozygosity is measured by comparing alleles at a locus
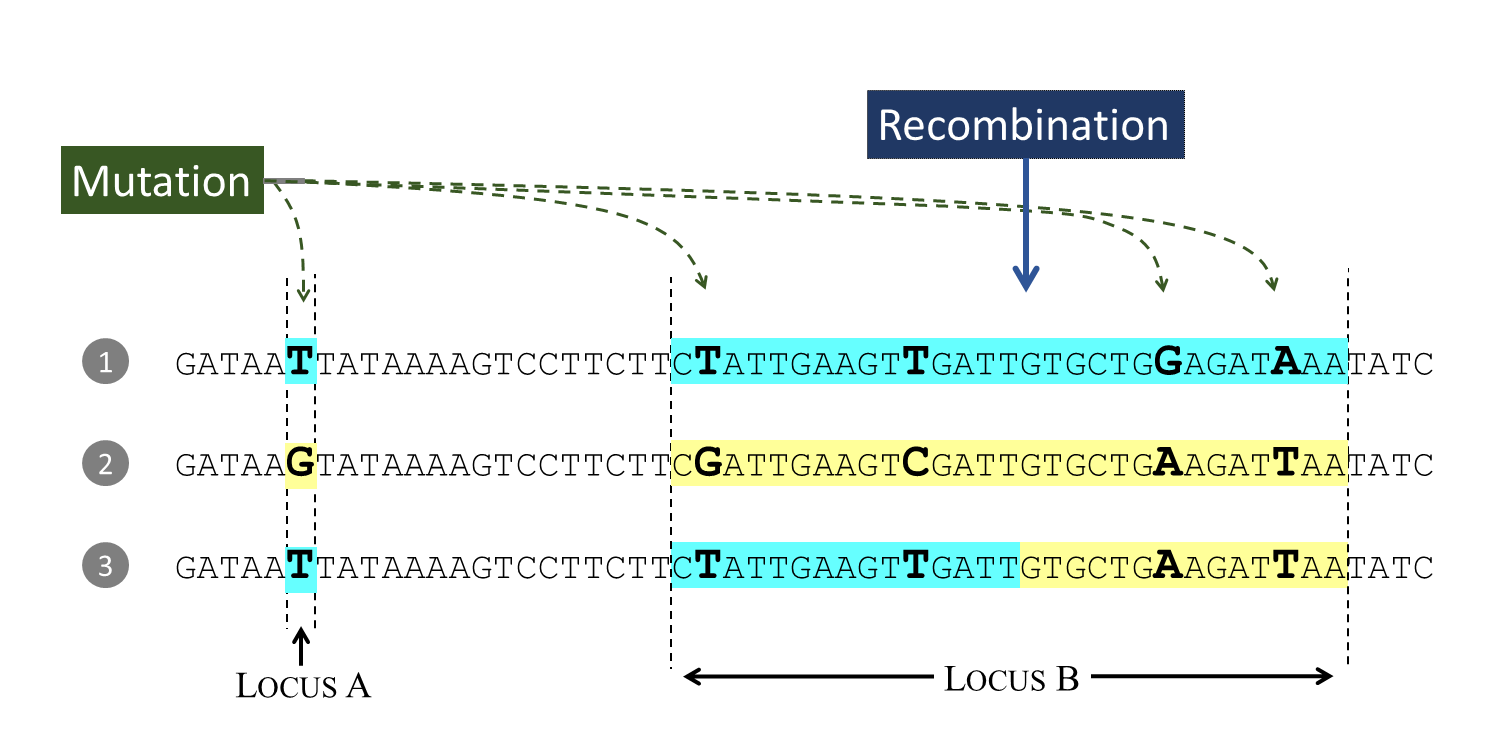 .
.
An allele is an instance of the parasite genome and a locus is a specific location in the genome. Here we see three alleles at two loci: locus A is a single nucleotide position (we call this a point locus) and locus B extends over multiple nucleotide positions (we call this a haplotype locus). Both loci have been affected by mutation, and locus B has also been affected by recombination.